|
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY |
|
Gas Chromatography is one of the most powerful, yet simplest, tools
of modern analytical chemistry. The idea is that a gas stream will be separated into its
atomic and/or molecular components when it is passed through a pipe packed
with a porous material. This
happens because each atomic or molecular particle sticks to the surfaces
of the packing material and is delayed in transit through the pipe in its
own unique way. Those
components of the gas stream which do not spend much time stuck to the
surfaces of the packing material move through the pipe faster that those
components which do, with all gradations in between.
The common practice is to use an inert carrier gas such as helium
to sweep the sample we wish to separate through the column and to detect
the components as they emerge from the far end.
The physics of diffusion in solids is similar in many ways, except
that there is no carrier gas, and we may find the term "solid
chromatography" useful to describe the age dating process I am
proposing here.
I was introduced to GC when Varian bought a small company making
gas chromatographs for sale as analytical instruments.
The lore, as it came down to me, was that this start-up company was
an outgrowth of a Department of Agriculture research grant for the study
of strawberry flavor leading to a method for synthesizing it.
Philosophical arguments as to the wisdom of such an undertaking
aside, the proposal was that the aromatic oils carrying the flavor of
strawberry could be separated using a column, analyzed component for
component, and then synthesized from inexpensive products.
A sample of strawberry oil was introduced into an inert gas stream
flowing through a pipe packed with a porous material.
The gas coming out of the exhaust end of the pipe was passed over a
slowly rotating drum cooled by liquid nitrogen.
The carrier gas would not condense at this temperature, but the
components of the oil were frozen out as discrete deposits on the surface
of the drum. The individual
deposits were then scraped off and analyzed to determine their organic
structure. The original
compound was subsequently reconstructed using the same oils in
approximately the correct proportions from sources having nothing to do
with strawberries.
I have no way to prove or disprove my suspicion that the synthetic
strawberry flavor might fool the buying public, but that any discerning
person could readily tell the difference between the synthetic flavor and
the real thing. All living
things, from single cell organisms to human beings, are extraordinarily
adept at complex pattern recognition and comparison.
I am very curious, but it is not clear to me how it all works.
One of the great triumphs of modern science is the Kinetic Theory
of Gases. The ancient Greeks
recognized only 4 basic building blocks in Nature... Earth, Air, Fire, and
Water. When I was in high
school, we had 92 elements, from Hydrogen to Uranium, and 3 states of
matter... solids, liquids, and gases.
There was no mention of plastics or living tissue.
We also had an unlimited number of compounds of atoms, called
molecules, among which H2O, water, was the most familiar[1].
Solids, we were told, were characterized by atoms bound to each
other in orderly arrays, like ice crystals for instance.
Solids might bend and stretch slightly, but they tended to hold
their original shape. Liquids
were characterized by atoms in close proximity, but without structure and
not so strongly bonded to each other as they flowed more or less freely
past each other, water being a prime example.
Gases are characterized by atoms or molecules separated from each
other, on the average, by distances large compared to the size of the
particles. They are in
constant motion, frequently colliding with one another, essentially free
and independent of all other particles in the gas.
Air, for example, was cited as a near perfect gas composed of
roughly 80% Nitrogen and 20% Oxygen with a density roughly 1/1000 that of
water. Steam, I learned later
in college thermodynamics, was somewhat like a gas, but it did not obey
the gas laws very well at ordinary temperatures because of a strong
tendency to condense and become a liquid.
An ideal gas, according to the Kinetic Theory, is an assemblage of
atoms or molecules wherein essentially all of the energy of the system is
stored in the kinetics of linear motion. In his classic study of gravity some 400 years ago, Sir.
Isaac Newton found it convenient to describe two mathematical forms which
he called energy. In one
form, a force, such as the force of gravity on a massive object, acting
through a distance, was found to result in a change in the velocity of the
mass in a precise way. The
quantity associated with velocity without regard to a force field was
referred to as Kinetic Energy, while the quantity associated with motion
in a force field without regard to velocity was referred to as Potential
Energy. After centuries of
wrangling, it is now generally agreed among all right thinking scientists
that the total energy, being the sum of the potential energy and the
kinetic energy, is a constant in any closed system.
In general, the total kinetic energy of an ideal gas is directly
proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
The kinetic theory thus gives us an absolute scale of temperature.
No gas is perfectly ideal because there is always a slight amount
of the total energy involved in the attractive forces between the gas
particles as potential energy. As
the temperature is reduced, the particles move more slowly and the
potential energy associated with the attractive forces becomes a greater
fraction of the total energy and all gases will eventually form liquids.
Helium is the most ideal gas, but it will become a liquid near the
absolute zero of temperature. Steam
is far from an ideal gas and will liquify at sea level at 100 DgC.
When gas particles, atoms or molecules, approach a solid surface
there is, except in some special circumstances, a repulsive force which
causes the particle to come to rest, reverse course, and re-enter the gas
phase. The pressure on the
walls of a closed container may be calculated from Newton's Laws of Motion
as the sum of the forces required to keep the gas confined, averaged over
the entire population of gas particles enclosed.
However, a small fraction of the gas particles approach the surface
at such high velocity that there is a finite probability that the particle
will become stuck to the surface somehow.
A range of scenarios seem to be possible.
If the gas particle is an atom, it may penetrate the surface and
become lodged at or below the surface.
If it is a molecule, it may break apart into its constituent atoms,
each of which will, most likely, become stuck.
There is also the possibility that a molecule may become stuck on
the surface intact. Considerable
evidence exists to suggest that a molecule must first be disassociated
into its atomic components before it can be absorbed into a solid lattice
below the surface. Once an atom or molecule has become bonded in some way to a
solid surface, there is a finite probability that it will reside on or
near the surface for a while and then re-enter the gas phase. There is also a small, but finite, probability that atoms
which become trapped within the solid will diffuse deeper and may re-enter
the gas phase sooner or later or, perhaps, never.
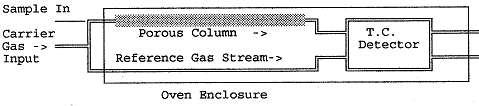
A typical configuration of a gas chromatograph is shown
schematically below:
The carrier gas flow is split between a reference channel and the
main separation column, all enclosed in a well insulated constant
temperature oven. The gas
coming out of these two channels is passed through a thermal conductivity
(TC) detector bridge described in further detail below. The detector is included in the oven. The carrier gas source is typically a tank of helium or dry
hydrogen and the flow is adjusted using a soap bubble device at the
exhaust end of each channel.
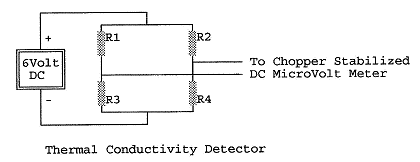
The thermal conductivity detector is shown schematically here:
Thermal Conductivity Detector
The thermal conductivity detector consists of four equal
temperature sensitive resistors in a bridge configuration.
A typical detector element might consist of a coil of gold plated
tungsten wire of roughly 30 ohms, or perhaps a thermistor.
Each resistor is housed in its own chamber in a copper block which
is kept at a constant temperature in the oven.
The gas stream emerging from the separation column passes through
chambers containing R1 and R4 while the gas emerging from the reference
channel passes through chambers containing R2 and R3.
When there are no molecules or atoms other than those of the
carrier gas in both channels, the thermal conductivity of the gas in all
four chambers is equal, the resistors are all at the same temperature, and
the bridge is balanced. We typically use an external bias at the input of the DC
microvolt meter to compensate for any slight differences in the resistors
and balance the bridge in this way. When
there are atoms or molecules other than those of the carrier gas
surrounding R1 and R4, the thermal conductivity of the gas, hence the
temperature, hence the resistance of R1 and R4 changes and the bridge goes
out of balance. This event is
noted on a chart recorder driven by the output of the DC microvolt meter.
Soon after Varian went into the GC business, I was assigned to
investigate some problems with the TC detector elements.
These were purchased from a sole source vendor.
The cost was high, the delivery erratic, and the quality poor.
The GC people were eager for my help and provided me with accounts
of the theory as well as the bits and pieces necessary to make my own
instrument so I could study the problem first hand at my own facilities.
I soon had a portable system completely self contained on a tea
wagon.
When the oven and TC detector have come to a stable temperature and
the carrier gas flow rates in the two channels are constant, a separation
run may be initiated by introducing a small sample into the carrier gas
entering the separation column as indicated in the above schematic.
A wide variety of methods are used depending on the nature of the
sample, but volatile liquids are often introduced using a hypodermic
needle through a thick rubber gland. There is always a change in pressure and flow rate when the
sample is introduced which is detected at the TC detector and recorded as
a transient marking the start of the run.
After a time, the most mobile component of the sample enters the TC
detector and the event is recorded. A
while later, the next most mobile component comes out and leaves a record,
and so on until all, or almost all, of the components of the sample have
passed through the column. The
recorder chart presents a spectrum, or a fingerprint, of the sample broken
down into its molecular or atomic components.
The fingerprint of a specific sample will depend on the nature of
the porous packing material in the separation column and on the
temperature. The general
effect of increasing the temperature is to compress the spectrum by
decreasing the time required for each component to come through.
The choice of packing material depends greatly on the types of
specimens to be separated. Water,
for example, is so tightly bonded to some materials that the time required
for these molecules to emerge at the exit end of the column could be
longer than we are prepared to wait.
This problem might be overcome, however, if we have the ability to
increase the temperature of the oven sufficiently.
In most cases, the spectral lines which make up the fingerprint
characteristic of specific molecules have the familiar shape of a Normal,
or Gaussian, distribution. There
is a good reason for this in a mathematical finding called the Central
Limit Theorem in Statistics which was proposed by Gauss in the last
century. Roughly speaking,
this theorem states that the distribution of a random variable which can
be expressed as the sum of random components tends to be Gaussian, or
Normal, in many cases. The
main restriction is that no one of the components is allowed to dominate
the process. To illustrate
this theorem in a way intended to appeal to the reader's intuition,
consider an often repeated trip such as one between home and work.
If we keep careful records of the transit time for several months
and then conduct a statistical analysis of the results, we are apt to find
that the distribution is roughly Gaussian about some average time.
The total trip can always be broken down into arbitrary components,
such as trips between traffic lights and stop signs and points of
congestion where there is merging traffic.
Each of these components has an average, or expected, transit time
with a degree of uncertainty. On rare occasions, all or most of the components could be on
the rapid transit side of the uncertainties.
On the other hand, we might catch every red light.
More frequently, however, the good and bad fortune will tend to
nullify each other and we will arrive at the expected time, give or take a
little. All bets are off if
there is a street level railroad crossing where we might occasionally
catch a slow freight and be held up for half an hour.
The transit time of a population of specific molecules through a GC
column depends on a number of factors.
We can assume that the molecules of the specimen drift at the
velocity of the carrier gas when they are not trapped on the surface of
the packing material. We can
also assume that not every collision between a molecule of the specimen
and the surface results in entrapment, although some do. Once trapped, the specimen molecule can be expected to dwell
for a statistically predictable time depending on the binding energy and
the temperature. When we get
around to discussing diffusion in solids, we will revisit this concept in
some detail.
Not all GC spectral lines are Gaussian Normal.
The column I had to work with was packed with a proprietary
molecular sieve with the trade name Zeolite.
I used the instrument quite often as a leak detector looking for
air in Argon or Helium filled welding boxes and reducing atmosphere
furnaces. The least expensive
commercial reducing atmosphere is disassociated ammonia, NH3.
Varian had a cracking unit to effect the reaction 2NH3
-> N2 + 3H2.
I almost always used a tank of dry hydrogen as the carrier gas, so
introducing a sample from a furnace containing disassociated ammonia
always produced a characteristic Nitrogen spectral line.
Argon is roughly 1% of the atmosphere while Oxygen is roughly 20%,
so the presence of Argon and Oxygen in the spectrum was compelling
evidence of a leak somewhere in the furnace or the feed lines.
The Argon and Oxygen lines, when present, were properly Gaussian
while the Nitrogen line was markedly skewed.
The rationale for the shape of the Nitrogen line was that the
probability of attachment was very low leading to relatively few
attachments, while the dwell time was long and tended to dominate the
process.
By itself, the spectrum of a gas sample as recorded using a TC
detector is not very useful for determining the atomic or molecular
component species involved. Additional
information is required and this may be found in a variety of ways.
In the case of strawberry flavor, the components were separated and
frozen and analyzed by other methods.
In some cases, the emerging components may be passed through a
flame and identified by their optical spectrum.
Gas chromatographs have also been used in conjunction with a mass
spectrometer whereby the emerging components from the GC column are passed
over a permeable membrane at the input of the mass spectrometer.
Certain components emerging from the GC column diffuse through this
membrane, which excludes the carrier gas, and enter the mass spectrometer
where the mass of the molecules are determined.
In other cases, we know what molecules we are apt to find and
calibrate the system by introducing a known sample and recording the
transit time for each component. The
area under the response curve is roughly proportional to the amount of the
emerging component and this can often be calibrated as well using a known
sample.
The chemistry department at Varian came up with a very neat method
for determining the carbon content of nickel and iron using GC.
The metal sample is burned to completion in a flow of pure Oxygen
while the gases down stream are passed through a Nichrome tube at liquid
nitrogen temperature. Any CO2
in the gas stream is frozen out in the Nichrome tube.
This tube is then connected in series with the separation column of
a GC calibrated with a know CO2 sample.
After the TC detector has been stabilized, the Nichrome tube is
heated electrically and the amount of CO2 released is
determined with great precision and sensitivity.
This process could have been used very successfully to measure the
sulphur content of stainless steel, but no one thought of it at the time.
The surface bonding and release mechanisms in certain simple cases
can be described in terms of a model wherein an atom or molecule in the
near vicinity of a solid surface experiences a repulsive force increasing
in magnitude as the separation decreases until a certain point is reached
at which the force becomes attractive for a short interval and then
repulsive again. The
potential energy profile is sharply increasing with decreasing distance
except for a potential energy well very close to the surface.
The energy required to get close enough to the surface to become
trapped in this energy well is sometimes referred to as the heat of
adsorption. Once trapped,
the energy required to escape and re-enter the gas phase is sometimes
referred to a the heat of desorption.
Adsorption is a term used to describe a surface reaction
wherein the adsorbed gas particle remains intact on the surface.
Absorption is a term used to describe a surface reaction
wherein the absorbed gas particle is disassociated into its atomic
components which take up residence within the solid, most likely below the
surface. A range of scenarios
is possible.
The heat of adsorption may be either positive or negative.
An H2O molecule, for example, approaching the surface of
liquid water at room temperature will experience a near 100% probability
of sticking, releasing the heat of vaporization in the process.
An N2 molecule, on the other hand, approaching a pure
tungsten surface will absorb energy and refrigerate the system when, on
rare occasions, it becomes bonded. The
main problem I had to address with regard to TC detector elements had to
do with surface chemistry between the components in the gas stream and the
resistance wire. Pure
tungsten was the resistor element of choice, for reasons which were never
made clear to me, and it was gold plated to minimize the thermal effects
of surface chemistry between the tungsten and the species emerging from
the GC column. The adherence
and porosity of the gold plating were not easy to control, but as soon as
our supplier learned that we were looking into the matter, he soon found
ways to correct these and other shortcomings of his detector elements.
Before I was taken off the GC project and given other assignments,
I had occasion to use the GC to separate Hydrogen in a gas sample.
This required the use of a carrier gas other than Hydrogen.
Helium was a possible choice, but I used Argon instead because of
the greater contrast in thermal conductivity between Hydrogen and Argon. This arrangement worked very well, but when I switched the
carrier gas back to Hydrogen I was quite surprised to find that several
days were required before the TC detector could be stabilized even at the
maximum possible oven temperature. I
assume that the column somehow retained great quantities of Argon and
released it very slowly. Perhaps
the Argon found its way deep into the small pores of the column packing
and did not have occasion to enter the carrier gas stream between being
liberated at one site and being trapped at the next site.
I never found a completely satisfactory explanation of this
phenomenon, but then I only saw it once and never had a chance to study
the matter in any depth. A
wide range of scenarios is to be expected in GC, and I suppose that is
also the case in Solid Chromatography.
As a general rule, though, when physical processes do not obey
simple models, the discrepancies are almost invariably clues to
interesting discoveries of new principles. [1]There
was also the story about the football star who had to pass a chemistry
test in order to be eligible to play in the big game upcoming.
It was decided to give him an oral exam... with only one
question... "What is H2SO4?"
He thought about it for several minutes and then said,
"Well, it ain't water."
"You pass", said the examiner.
|